Brain Health vs. Mental Illness: A Comprehensive Comparison
The Key Differences Between Brain Health and Mental Illness
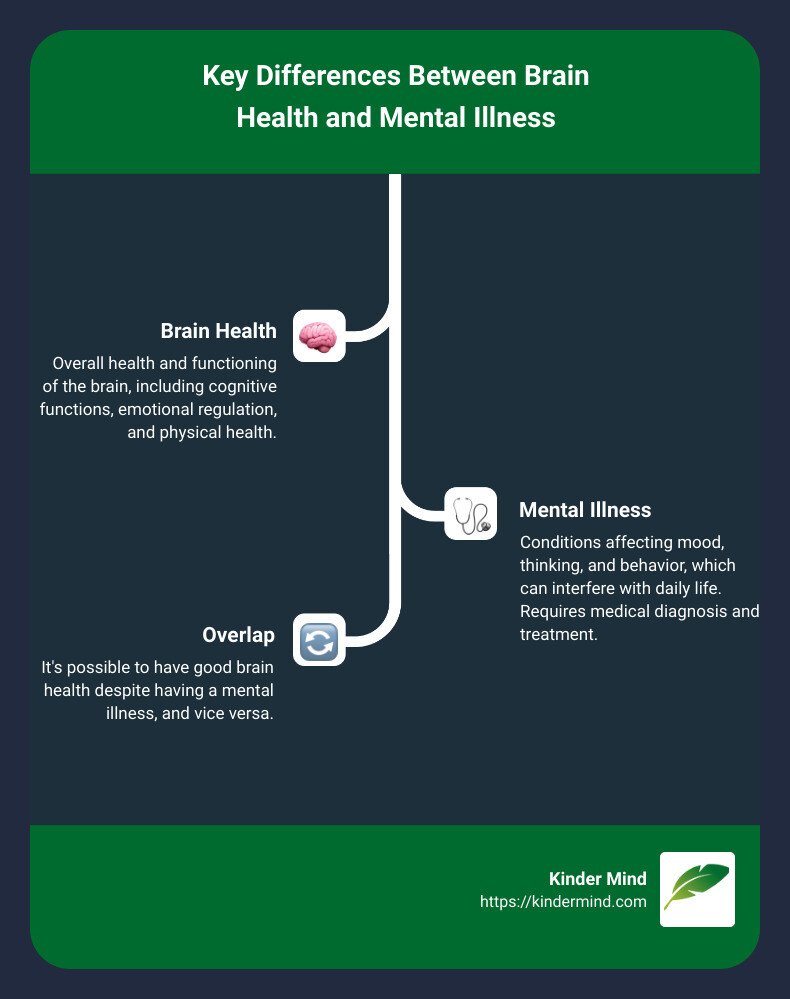
When it comes to mental wellbeing, understanding the difference between brain health and mental illness is crucial. Though these terms are often used interchangeably, they actually refer to distinct aspects of our mental state:
Brain Health: Refers to the overall health and functioning of your brain, including cognitive functions, emotional regulation, and physical health.
Mental Illness: Encompasses a range of conditions that affect your mood, thinking, and behavior, which can interfere with daily life.
Key Differences:
Brain Health: Everyone can work to improve it, similar to physical fitness.
Mental Illness: Specific conditions that require medical diagnosis and treatment.
Overlap: You can have good brain health despite having a mental illness, and vice versa.
I am Dr. Elizabeth Barlow, founder of Kinder Mind. With my experience in virtual mental health services, I focus on demystifying complex topics like brain health vs mental illness to make mental wellness accessible to everyone.
In the next section, we'll delve into what brain health really means and why it matters.
Understanding Brain Health
Factors Affecting Brain Health
Brain health is about keeping your brain in top shape. It includes various aspects like cognitive health, sensory health, emotional regulation, and physical health. Let's break down the key factors that affect brain health:
Diet: Dr. Uma Naidoo, a nutrition expert, emphasizes that "the food we eat has a direct impact on our brain function, including our mood, memory, and cognitive abilities." Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can boost brain health.
Exercise: Regular physical activity is crucial. It improves blood flow to the brain and encourages the growth of new brain cells. Exercise is also linked to better mood and reduced stress.
Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for brain health. During sleep, the brain repairs itself and consolidates memories. Lack of sleep can impair cognitive functions and emotional regulation.
Mental Stimulation: Engaging in activities that challenge your brain, like reading, puzzles, or learning new skills, can keep your brain sharp. Mental stimulation encourages the formation of new neural connections.
Stress Management: Chronic stress can have negative effects on the brain, leading to issues like memory impairment and increased risk of mental illness. Techniques like mindfulness, yoga, and deep breathing can help manage stress.
Importance of Brain Health
Maintaining good brain health is vital for overall wellbeing. Here are some key reasons why it's important:
Cognitive Function: A healthy brain supports learning, reasoning, and problem-solving. It allows you to process information efficiently and make informed decisions.
Decision-Making: Good brain health helps you make better choices in daily life. It enhances your ability to weigh options, consider consequences, and act decisively.
Memory: A healthy brain is crucial for retaining and recalling information. It helps you remember important details, from daily tasks to cherished memories.
Emotional Wellbeing: Brain health affects how you regulate emotions. A well-functioning brain can help you manage stress, anxiety, and mood swings, leading to better emotional balance.
By focusing on these factors, you can improve your brain health and enhance your quality of life.
In the next section, we'll explore the symptoms and types of mental illness, shedding light on how they differ from brain health issues.
What is Mental Illness?
Mental illness refers to a range of mental health conditions that affect a person's mood, thinking, and behavior. These conditions can interfere with daily life, making it difficult to function effectively.
Symptoms of Mental Illness
Mental illnesses manifest in various ways, often impacting mood, thinking, and behavior. Here are some common symptoms:
Mood Changes: Frequent mood swings, extreme sadness, or irritability.
Anxiety: Persistent worry, fear, or panic attacks.
Depression: Feelings of hopelessness, fatigue, and loss of interest in activities.
Behavioral Changes: Withdrawal from social activities, changes in eating or sleeping patterns.
Cognitive Issues: Trouble concentrating, memory problems, or difficulty making decisions.
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it's crucial to seek help from a mental health professional.
Types of Mental Illness
Mental illnesses can be categorized into various types, each with its own unique set of symptoms and treatment options.
Depression: Also known as Major Depressive Disorder, this condition goes beyond occasional sadness. It includes profound lows, difficulty focusing, and extreme fatigue. Severe cases may lead to psychotic symptoms like delusions and hallucinations. However, with the right support and medication, individuals can lead fulfilling lives.
Anxiety Disorders: These include generalized anxiety disorder, phobias, and panic disorders. Symptoms can range from a general feeling of unease to severe panic attacks. About 31% of adults will experience an anxiety disorder in their lifetime. Treatments include therapy, medication, and relaxation techniques.
Bipolar Disorder: This condition involves dramatic mood swings between extreme energy (mania) and deep depression. Managing bipolar disorder often requires a combination of medication and cognitive-behavioral therapy.
Schizophrenia: A severe mental disorder affecting how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. Symptoms may include hallucinations, delusions, and disordered thinking. Treatment typically involves antipsychotic medications and supportive therapies.
Personality Disorders: These are long-term patterns of behavior and inner experiences that differ significantly from what is expected. Examples include Borderline Personality Disorder and Antisocial Personality Disorder. Treatment often involves psychotherapy.
Understanding these conditions is the first step toward seeking appropriate treatment and support.
In the next section, we'll delve into how mental illness affects brain health and the importance of maintaining good brain health.
Brain Health vs. Mental Illness
How Mental Illness Affects Brain Health
Mental illness and brain health are closely linked, but they are not the same thing. Mental illness refers to conditions that affect a person's thinking, feeling, mood, or behavior. Brain health involves optimal cognitive, emotional, and social functioning without disease or damage.
Mental illnesses can significantly impact brain health. According to Dr. Amen, mental health disorders can cause changes in brain function and structure. For example, depression has been linked to a decrease in the size of the hippocampus, which is responsible for memory and learning.
Brain Areas Affected by Mental Illness
Hippocampus: Depression can shrink this area, affecting memory and learning.
Amygdala: Anxiety can heighten activity here, leading to increased fear and vigilance.
Prefrontal Cortex: Depression can disrupt this area, making it harder to regulate emotions and make decisions.
Mental illness also affects neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers in the brain. Imbalances in neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine can lead to disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Maintaining Good Brain Health
Maintaining good brain health is crucial for mental wellbeing. Here are some steps to keep your brain in top shape:
Healthy Diet
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats provides the nutrients and antioxidants needed to protect the brain. Dr. Uma Naidoo, a nutritional psychiatrist, emphasizes the importance of a balanced diet for optimal brain function.
Regular Exercise
Exercise increases blood flow to the brain, promotes the growth of new brain cells, and improves cognitive function. It also helps in managing stress, which can have a profound impact on brain health.
Sleep Hygiene
Getting enough sleep is crucial for brain health. Poor sleep can affect mood, memory, and cognitive function. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can lead to long-term changes in brain structure and function. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress.
Mental Challenges
Engage in activities that challenge your brain, such as learning a new skill, playing a musical instrument, or solving puzzles. These activities can strengthen neural connections and improve cognitive function.
Summary
Understanding the difference between brain health and mental illness is crucial. While mental illness can negatively impact brain health, taking proactive steps like maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, getting enough sleep, managing stress, and engaging in mental challenges can help maintain good brain health and overall mental wellbeing.
Next, we'll explore the connection between brain health and mental illness, including the role of neurotransmission and the impact of stress on brain function.
The Connection Between Brain Health and Mental Illness
Mental Illness and Dementia Risk
Mental illness and dementia are deeply intertwined. Research shows that early life mental disorders can increase the risk of developing dementia later in life. For example, a study involving 1.7 million New Zealand citizens found that individuals with mental health conditions had a higher likelihood of cognitive decline and dementia as they aged.
This connection is partly due to changes in brain structure caused by mental illnesses. Conditions like depression and bipolar disorder can disrupt areas of the brain such as the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, impacting memory and decision-making. These disruptions can lead to long-term damage if untreated, increasing the risk of dementia.
Early intervention is key. Treating mental disorders early can reduce the risk of cognitive decline and dementia. This underscores the importance of recognizing and addressing mental health issues promptly.
Stress and Brain Health
Stress is another significant factor that affects both brain health and mental illness. Chronic stress can lead to mental illnesses such as depression and anxiety. It can also cause changes in the brain's structure and function, leading to memory impairment and cognitive decline.
When we experience stress, our brain releases neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. These chemicals help regulate mood, motivation, and cognitive function. However, chronic stress can disrupt their balance, leading to mental health issues.
Studies show that prolonged stress can increase the production of myelin-producing cells, which affects the brain's white matter. This can interfere with the timing and balance of communication between neurons, leading to cognitive and emotional problems.
Moreover, stress affects the hippocampus, a critical area for memory and learning. Chronic stress can shrink the hippocampus, impairing memory and increasing the risk of mental illnesses and cognitive decline.
Taking steps to manage stress is crucial for maintaining brain health. Techniques like regular exercise, mindfulness, and adequate sleep can help mitigate the harmful effects of stress on the brain.
By understanding the connection between brain health and mental illness, we can better address the risks and take proactive measures to maintain overall mental wellbeing.
Next, we'll address some frequently asked questions about brain health and mental illness, including the differences between brain illness and mental illness and the link between the brain and mental health conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions about Brain Health vs. Mental Illness
What is the difference between brain illness and mental illness?
Brain illness and mental illness are terms that are often used interchangeably, but they refer to different aspects of our mental wellbeing.
Brain illness typically involves physical changes or damage to the brain. This can result from physical trauma, such as a head injury, or conditions like Alzheimer's disease that physically alter the brain's structure. Brain illnesses can affect brain function, leading to issues with learning, reasoning, and memory.
Mental illness, on the other hand, primarily affects a person's mood, thoughts, and behaviour. Conditions like depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder are examples of mental illnesses. These conditions are often influenced by psychological pressures and environmental factors, rather than physical changes in the brain.
Is there a link between the brain and mental illness?
Yes, there is a significant link between the brain and mental illness. Mental illnesses often stem from disruptions in neuron communication and neurotransmission.
Neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine play critical roles in regulating mood and emotions. For instance, low levels of serotonin are commonly associated with depression.
Moreover, mental illnesses can impact specific areas of the brain. For example, anxiety can heighten activity in the amygdala, leading to increased fear and vigilance. Depression can disrupt the function of the prefrontal cortex, making it harder to regulate emotions and make decisions.
What is the difference between cognitive health and mental health?
Cognitive health refers to the brain's ability to perform tasks related to learning, reasoning, and memory. Good cognitive health means your brain is functioning well, allowing you to think clearly, make decisions, and remember important information.
Mental health, however, encompasses your overall emotional wellbeing and psychological wellbeing. It includes how you feel, how you handle stress, and how you relate to others. While cognitive health is a part of mental health, mental health also covers emotional aspects like happiness, stress levels, and resilience.
By understanding these differences, we can better address both cognitive and emotional aspects to maintain overall mental wellbeing.
Next, let’s explore how maintaining good brain health can prevent mental illnesses and improve overall quality of life.
Conclusion
Understanding brain health vs. mental illness helps us see the bigger picture of our mental wellbeing. Brain health focuses on keeping our brain functioning well. This includes our ability to think, and make decisions. On the other hand, mental illness refers to specific conditions that affect our mood, thinking, and behavior.
At Kinder Mind, we believe in a holistic approach to mental wellness. This means we consider both brain health and mental illness when offering care. Our goal is to help you understand and take care of your mental health proactively.
Proactive Care
Taking a proactive approach to mental health involves more than just addressing symptoms. It includes:
Healthy Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can improve brain function.
Regular Exercise: Physical activity boosts blood flow to the brain and promotes the growth of new brain cells.
Adequate Sleep: Good sleep hygiene is crucial for both brain health and mental health.
Stress Management: Techniques like mindfulness and meditation can help manage stress and improve overall wellbeing.
Mental Challenges: Engaging in activities that challenge your brain, like learning a new skill, can keep your mind sharp.
By adopting these habits, we can improve our brain health and reduce the risk of mental illness.
Holistic Approach
Our holistic approach integrates both physical and mental health. We believe that by taking care of our brain, we can improve our overall quality of life. This involves understanding the connection between brain health and mental illness, and taking steps to maintain both.
For personalized therapy sessions that focus on both brain health and mental illness, schedule your session with Kinder Mind today. Let's work together to achieve mental wellness and a healthier brain.
In summary, understanding the distinction between brain health and mental illness is crucial. It allows us to take a comprehensive approach to our mental wellbeing. At Kinder Mind, we are committed to helping you navigate this journey with compassion and expertise.